Introduction
Key points
About EMIT Data
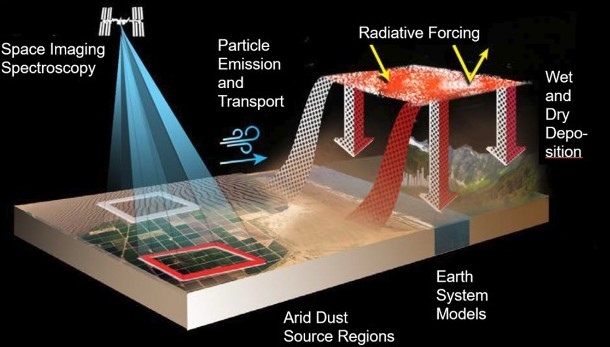
EMIT (Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation) is a NASA mission that aims to measure the mineral composition of dust sources on Earth's surface. It seeks to understand how these mineral dust particles affect the Earth's environment, particularly their heating and cooling effects through radiative forcing. The mission uses remote sensing and satellite technology to gather critical data for climate research and environmental science.
There are two main objectives:
About Cape Region
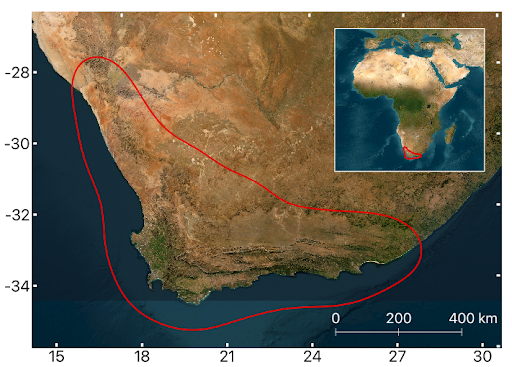
As it is currently acknowledged, there are six floral kingdoms in the world. The South African Kingdom is the smallest among them, encompassing only the Cape region, covering approximately 90,000 square kilometers. The Cape region of South Africa stands out as one of the most extraordinary biodiversity hotspots, boasting a flora that comprises over 9,000 plant species, with nearly 70% of which are endemic. Unfortunately, this area is also under threat of, changing wildfire regimes, habitat destruction and climate change. We need to take action!